Photo by Mohammad Rahmani on Unsplash
How to use Git and GitHub for your personal Project
Learn to use Git and GitHub to carry out Version Control on your Project
Since we know Git helps to save versions of our project(code) so that we can refer to any version over time, We will use it to save versions of our code with the following example:
Let's say you want to build a very simple calculator program using python programming language. The calculator program will be able to carry out addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication.
First, you will create a python file named "calculator.py". In the file at first, let's say you have the following code:
userresponse = int(input("Enter 1 to add two numbers, 2 to subtract, 3 to multiply and 4 to divide: "))
if userresponse == 1:
firstnumber = int(input("Enter firstnumber: "))
secondnumber = int(input("Enter secondnumber: "))
print("The sum is: ", firstnumber + secondnumber)
to save this version of the code using git:
You have to first initialize a git repository. Run the following command on your project's terminal:
git initAn empty git repository or folder will be created for you. Your changes will be saved to that folder.
Next, you will stage the file. Staging is adding your file to an area or file before actually saving. You can think of it as putting up your file for saving or commit.
git add calculator.py
Note: calculator.py should be replaced with your own file name and extension.
To add multiple files, you can use: git add NAMEOFFILE NAMEOFFILE
To add all files with changes: git add .
You can run "git status" to see the status of your project
And then commit(save) the staged file. Run the following command on the terminal:
git commit -m "Add code to sum two numbers"
"Add code to sum two numbers" is the commit message. When you commit, you need to supply a message describing why you made your change.
Once you commit the file(code), the code is saved and you can recall it at any point in your project.
Add more code to your calculator.py file for subtraction, multiplication, and division.
elif userresponse == 2:
firstnumber = int(input("Enter firstnumber: "))
secondnumber = int(input("Enter secondnumber: "))
print("The difference is: ", firstnumber - secondnumber)
elif userresponse == 3:
firstnumber = int(input("Enter firstnumber: "))
secondnumber = int(input("Enter secondnumber: "))
print("The multiplication is: ", firstnumber * secondnumber)
elif userresponse == 4:
firstnumber = int(input("Enter firstnumber: "))
secondnumber = int(input("Enter secondnumber: "))
print("The division is: ", firstnumber / secondnumber)
else:
print("Invalid response.")
Your complete program should be as below:
userresponse = int(input("Enter 1 to add two numbers, 2 to subtract, 3 to multiply and 4 to divide: "))
if userresponse == 1:
firstnumber = int(input("Enter firstnumber: "))
secondnumber = int(input("Enter secondnumber: "))
print("The sum is: ", firstnumber + secondnumber)
elif userresponse == 2:
firstnumber = int(input("Enter firstnumber: "))
secondnumber = int(input("Enter secondnumber: "))
print("The difference is: ", firstnumber - secondnumber)
elif userresponse == 3:
firstnumber = int(input("Enter firstnumber: "))
secondnumber = int(input("Enter secondnumber: "))
print("The multiplication is: ", firstnumber * secondnumber)
elif userresponse == 4:
firstnumber = int(input("Enter firstnumber: "))
secondnumber = int(input("Enter secondnumber: "))
print("The division is: ", firstnumber / secondnumber)
else:
print("Invalid response.")
You can commit or save this new change in your code, run the following command on your terminal to commit the new change:
git add calculator.py
git commit -m "Add code to calculate diff,mul and div"
Now, what if you want to return back to when you had code to sum two numbers then you have to revert the commit for when you added code to calculate the difference, product, and division of two numbers.
Run the following command on your terminal to see the log history of commits you have done so far:
git log --oneline
You will see the following result on your terminal:
1c5f696 (HEAD -> master) Add code to calculate diff,mul and div
9568fad Add code to sum two numbers
Notice the first commit has a shortened ID of "9568fad". Yours will be different, while the second commit has an ID of "1c5f696". We will use these ids to refer to any version of our project.
If you want to revert to when you had code to sum two numbers, you will revert 1c5f696 commit
git revert 1c5f696
When you run above command with your own commit ID, notice your code returned to when you had code to sum two numbers. That is one of the advantages of using Git, so by committing your changes, you are saving the changes so that you can refer to any version at any time either for analysis, or to undo changes, etc
Now, we are going to push our code to GitHub
Login to your GitHub account and create a new repository.
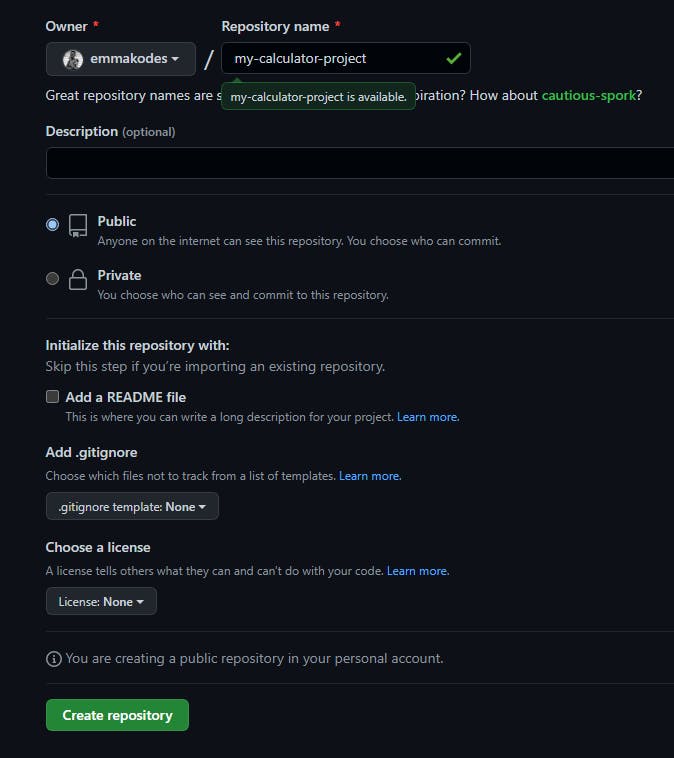
Give the repository a name, then you may leave every other option as default and click on Create repository
 Next, you return to the terminal of your project and run the following command,
Next, you return to the terminal of your project and run the following command,
git remote add origin https://github.com/emmakodes/my-calculator-project.git
Note: replace my-calculator-project with the name of your repository and emmakodes with your GitHub username
then run the following command to push your code:
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main
When you return to your repository on GitHub, you will find your code. You have just pushed your code to GitHub.
Check out:
