django-allauth is an integrated set of Django applications addressing authentication, registration, account management as well as 3rd party (social) account authentication. We will use this package to implement authentication workflow.
Create a new Django project and app
Create a new directory anywhere on your computer. You can do it on your desktop and then open the folder using your favorite code editor
Open the terminal and create a virtual environment using the following command
python -m venv .myvenvActivate the virtual environment
.myvenv\Scripts\activateInstall Django
pip install djangoStart a new Django project "userauth"
django-admin startproject userauth .Start a new Django app "accounts"
python manage.py startapp accountsRegister the Django app in the settings.py file of the Django project
# userauth/settings.py INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'accounts', # new ]
django-allauth
Install django-allauth
pip install django-allauthAdd the following config for django-allauth in settings.py
# userauth/settings.py INSTALLED_APPS = [ "django.contrib.admin", "django.contrib.auth", "django.contrib.contenttypes", "django.contrib.sessions", "django.contrib.messages", "django.contrib.staticfiles", "django.contrib.sites", # new # Third-party "allauth", # new "allauth.account", # new 'allauth.socialaccount', # new # Local "accounts", ] SITE_ID = 1 AUTHENTICATION_BACKENDS = ( # Needed to login by username in Django admin, regardless of `allauth` "django.contrib.auth.backends.ModelBackend", # `allauth` specific authentication methods, such as login by e-mail "allauth.account.auth_backends.AuthenticationBackend", ) # verification email will be sent to console EMAIL_BACKEND = "django.core.mail.backends.console.EmailBackend" # Controls the life time of the session. ACCOUNT_SESSION_REMEMBER = TrueGiven we have made changes to settings.py, let's run migrate to update our database
python manage.py migrate
URLs
Add the following code to the urls.py file of your Django project to configure URLs for django-allauth.
# userauth/urls.py from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include # new urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('accounts/', include('allauth.urls')), # new ]
Default Log-In and Sign-Up Pages
If you start up the local server now with python manage.py runserver you can navigate to the working log-in page at http://127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/login/
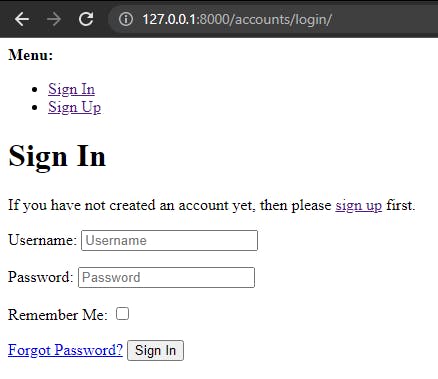
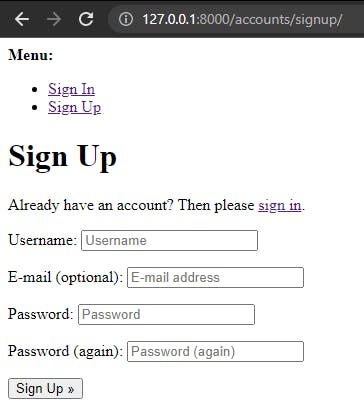
sign up page at http://127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/signup/
Style Templates
We will override the default login and Signup pages to declare templates that look better.
Create a folder 'templates' in the project root directory (the same folder you have the manage.py file). Then create another folder in the templates folder named 'account' as django-allauth looks for templates in the account directory.
Create a login.html and signup.html in templates/account directory and add the following code:
<!-- templates/account/login.html --> <h2>Log In</h2> <form method="post"> {% csrf_token %} {{ form.as_p }} <button type="submit">Log In</button> </form><!-- templates/account/signup.html --> <h2>Sign Up</h2> <form method="post"> {% csrf_token %} {{ form.as_p }} <button type="submit">Sign Up</button> </form>Update the TEMPLATES config in settings.py file to tell Django to look for the templates directory in the base directory.
# userauth/settings.py import os TEMPLATES = [ { ... 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')], # new ... } ]Start the development server and check out the newly styled login and signup page:
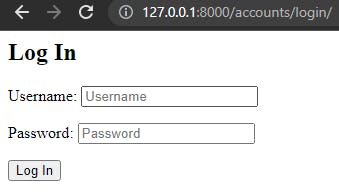
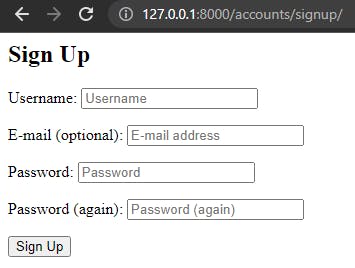
If you try out the forms you'll see they result in error pages, the reason because we need to tell Django where to redirect our users after they log in and log out.
You can create a superuser account by running the following command on the terminal:
python manage.py createsuperuser
Fill in your username, email, and desired password. You can log in to the admin page and ensure you log out before leaving the page.
Redirects
Add the following to settings.py to redirect the user to the 'home' URL name when the user logs in or log out.
# userauth/settings.py LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL = 'home' ACCOUNT_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URL = 'home'
We will create a new app for this new home URL
Run the following on the terminal to create a new Django app
python manage.py startapp newappAdd the new app to the list of installed apps.
# userauth/settings.py INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'django.contrib.sites', # 3rd party 'allauth', 'allauth.account', 'allauth.socialaccount', # Local 'accounts', 'newapp', # new ]Add it to the userauth/urls.py file.
# userauth/urls.py from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('accounts/', include('allauth.urls')), path('', include('newapp.urls')), # new ]Create a new urls.py file in newapp Django application and add the following code
# newapp/urls.py from django.urls import path from .views import HomePageView urlpatterns = [ path('', HomePageView.as_view(), name='home'), ]Add the following code to the views.py file of the newapp Django application to render home.html
# newapp/views.py from django.views.generic import TemplateView class HomePageView(TemplateView): template_name = 'home.html'Create the home.html file in templates/ directory and not templates/account directory. Add some basic logic for if the user is logged in or not.
<!-- templates/home.html --> {% if user.is_authenticated %} Hi {{ user.email }}! <p><a href="{% url 'account_logout' %}">Log Out</a></p> {% else %} <p>You are not logged in</p> <a href="{% url 'account_login' %}">Log In</a> | <a href="{% url 'account_signup' %}">Sign Up</a> {% endif %}
Test the complete system
Start the development server:
python manage.py runserverYou can test the whole system. Try to sign up, and log in from where you will see the homepage at https://127.0.0.1:8000/
That's it.
Thanks for reading

