Photo by Aaron Burden on Unsplash
How to build a user signup and login system using django-allauth and a custom user model. We will log in with Email instead of a username
We will learn to build a user sign-up and log-in system in Django with django-allauth package and a custom user model.
Create a new Django Project and app
Create a new directory anywhere. You can do it on your desktop and then open the folder on your favorite code editor
Open the terminal and create a virtual environment
python -m venv .myvenv
Activate virtual environment
.myvenv\Scripts\activate
Install Django
pip install django
Start a new Django project with a descriptive name. In my case, my project name is 'userauth'
django-admin startproject userauth .
Start a new Django app. In my case, app name is 'accounts'
python manage.py startapp accounts
Register the Django app in the settings.py file of the Django project and declare CustomUser as our user model instead of the built-in User model. Add the following code in the settings.py file of the Django project.
# userauth/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'accounts', # new
]
AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'accounts.CustomUser' # new
Configure a custom user model
I like to use a custom user model immediately, it provides flexibility in the future when you intend to make changes to the default user model
We will configure the user model to be able to log in with email. Open the models.py file in accounts directory and add the following code:
# accounts/models.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser
from django.db import models
class CustomUser(AbstractUser):
# add additional fields in here
def __str__(self):
return self.email
Create a forms.py file in your app 'accounts' directory and add the following code.
# accounts/forms.py
from django import forms
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm, UserChangeForm
from .models import CustomUser
class CustomUserCreationForm(UserCreationForm):
class Meta:
model = CustomUser
fields = ('username', 'email')
class CustomUserChangeForm(UserChangeForm):
class Meta:
model = CustomUser
fields = ('username', 'email')
Above, we are updating the two built-in forms: UserCreationForm and UserChangeForm to allow users sign up using the CustomUser model and also the superuser to be able to modify existing users using also the CustomUser model.
Update admin.py file
We will update the admin.py file in the accounts directory with the following code to allow Admin to use the CustomUser model.
# accounts/admin.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.contrib.auth import get_user_model
from django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin
from .forms import CustomUserCreationForm, CustomUserChangeForm
from .models import CustomUser
class CustomUserAdmin(UserAdmin):
add_form = CustomUserCreationForm
form = CustomUserChangeForm
model = CustomUser
list_display = ['email', 'username',]
admin.site.register(CustomUser, CustomUserAdmin)
Run the following command in your terminal to make a migrations file, migrate the database the first time, create a superuser so we can access the admin, and run the server. When you run the createsuperuser command, it will ask you for a username, email, and password, do enter those appropriately.
python manage.py makemigrations accounts
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py createsuperuser
python manage.py runserver
Configure Django all-auth
We are using django-allauth to configure authentication.
- Install django-allauth
pip install django-allauth
- Open settings.py file and add the following new settings which are needed by django-allauth
# userauth/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'django.contrib.sites', # new
# Third party
'allauth', # new
'allauth.account', # new
'allauth.socialaccount', # new
'accounts',
]
EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.console.EmailBackend'
AUTHENTICATION_BACKENDS = (
# Needed to login by username in Django admin, regardless of `allauth`
"django.contrib.auth.backends.ModelBackend",
# `allauth` specific authentication methods, such as login by e-mail
"allauth.account.auth_backends.AuthenticationBackend",
)
SITE_ID = 1
ACCOUNT_EMAIL_REQUIRED = True
ACCOUNT_USERNAME_REQUIRED = False
ACCOUNT_SIGNUP_PASSWORD_ENTER_TWICE = False
ACCOUNT_SESSION_REMEMBER = True
ACCOUNT_AUTHENTICATION_METHOD = 'email'
ACCOUNT_UNIQUE_EMAIL = True
- Run the migrate command
python manage.py migrate
URLs
We will add a path to django-allauth. Add the following code to urls.py in the project folder 'userauth'
# userauth/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include # new
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('accounts/', include('allauth.urls')), # new
]
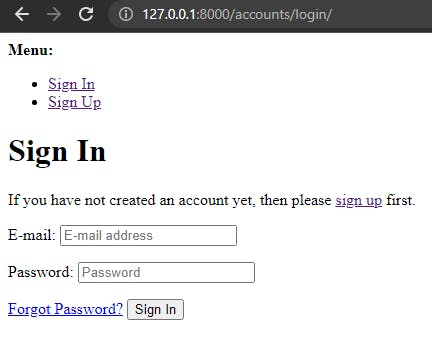
If you run the server and go to 127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/login you will get a page as the following:
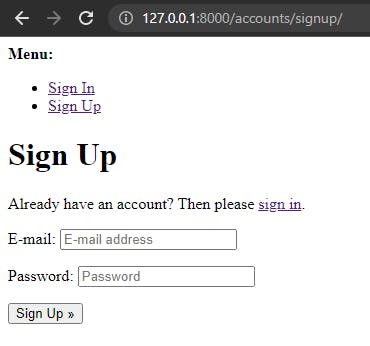
likewise for http://127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/signup/
To style these pages:
We will override django-allauth default login.html and signup.html files. django-allauth uses templates in an account folder so we'll override its defaults there.
Create a folder 'templates' in the base directory(the same directory you have manage.py file), then inside the templates folder, create another folder 'account'. Create a login.html and signup.html file inside the account folder
Place the following code in login.html
# templates/account/login.html
<h2>Log In</h2>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit">Log In</button>
</form>
Place the following code in signup.html
# templates/account/signup.html
<h2>Sign Up</h2>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit">Sign Up</button>
</form>
We will tell django to look for a templates folder in the project folder. Update the Templates config within the settings.py file with os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')
# userauth/settings.py
import os
TEMPLATES = [
{
...
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')], # new
...
}
]
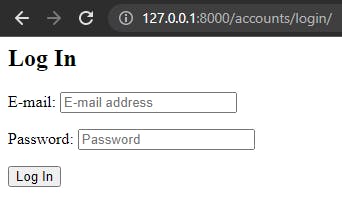
Start the development server and access 127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/login and http://127.0.0.1:8000/accounts/signup/ to see the new login and signup pages:
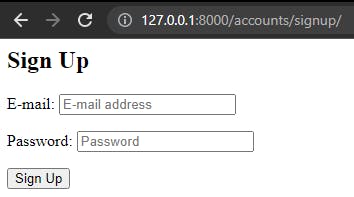
Redirects
We have to configure a redirect page so that when the user logs in or logout they will be redirected to that page.
Open settings.py file and add the following code to redirect to home URL name
# userauth/settings.py
LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL = 'home'
ACCOUNT_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URL = 'home'
Start a new django app 'newapp'. It can be any name(Use a more descriptive name)
python manage.py startapp newapp
Add the new app 'newapp' to our list of INSTALLED_APPS in settings.py file.
# userauth/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'django.contrib.sites',
# 3rd party
'allauth',
'allauth.account',
# Local
'accounts',
'newapp', # new
]
Create a URL path for the new app in urls.py file of your django project
# userauth/urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('accounts/', include('allauth.urls')),
path('', include('newapp.urls')), # new
]
Update the views.py file of 'newapp' with the following code.
# newapp/views.py
from django.views.generic import TemplateView
class HomePageView(TemplateView):
template_name = 'home.html'
Then make a new newapp/url.py file and add the following code:
# newapp/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from .views import HomePageView
urlpatterns = [
path('', HomePageView.as_view(), name='home'),
]
Create the home.html file in the templates directory (templates/home.html) and add some basic logic for if the user is logged in or not.
Be careful not to put this home.html within the templates/account directory, it is just to be in the templates itself. Add the following code in home.html
# te/home.html
{% if user.is_authenticated %}
Hi {{ user.email }}!
<p><a href="{% url 'account_logout' %}">Log Out</a></p>
{% else %}
<p>You are not logged in</p>
<a href="{% url 'account_login' %}">Log In</a> |
<a href="{% url 'account_signup' %}">Sign Up</a>
{% endif %}
Done. Make sure you are logged out by going to the admin page http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin
You can test it all out now.
Go to the homepage http://127.0.0.1:8000/ in your web browser to see the following page:
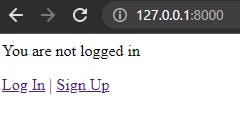
You can sign up and log in.
